Photo-Electric Effect

i. If f > fo, electrons are emitted out as well as accelerated. In this case, electrons carry the greatest kinetic energy.
ii. When f = fo, electrons are just emitted out but there is no acceleration. K.E. carried by electrons, in this case, is zero.
iii. If f < fo, emission of electrons is impossible but electrons are excited only.
• Incident light energy hf overcome binding energy, electrons are emitted out from the metal surface.
• During the emission, a single photon can emit out a single electron from the metal surface. (100% chance)
• The emission of no. of photo-electrons from the metal surface depends on the intensity of light.
• K.E. carried by emitted electrons depends on the frequency of light.
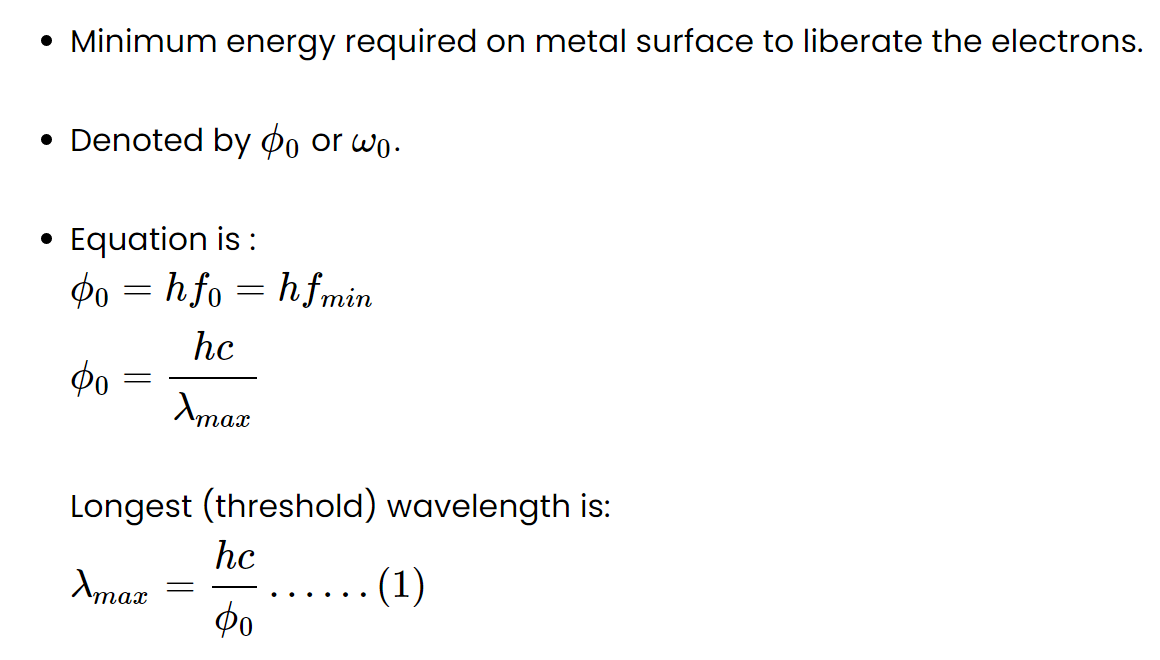
Work Function
Stopping potential
Einstein's photoelectric equation
• It deals with the conservation of energy. Energy neither be created nor be destroyed but can be changed from one form to another form. Before & after the emission of electrons, energy remains conserved.

Laws of the photoelectric effect
• The kinetic energy of the emitted electron is independent of the intensity of incident radiation
• Photo-electric current increases with the increase in the intensity of incident radiation.
• Kinetic energy of the emitted electron depends on the frequency of the incident radiation.
• KE increases with the increase of the frequency of incident radiation.
• Incident frequency should be greater than or equal to critical (threshold) frequency.
• There is no time lag between the arrival of light and the emission of photoelectrons.
• K.E. is directly proportional to (v – vo)
• Robert Andrew Millikan verified Einstein's photo-electric equation experimentally.
• When a graph is plotted in between the incident frequency and stopping potential graph represents a straight line with -ve intercept.

• Photo-cells are three types:
i. Photo-emissive
a. Vacuum type photo-emissive cells
b. Gas-filled type photo-emissive cells
ii. Photo-voltaic cells
iii. Photo-conductive cells
Uses of photo-cells:
• Photo-cells are used in photometry to compare the intensity of distinct sources.
• Highly used in counting & switching devices. • Used in alarm bells.
• Used in the one-way traffic light.
• Used in T.V. receivers.
• Used in photography.
• Used in industry.
• Photocells are used for automatic control of signals and detection of the speed of moving objects like vehicles on the roads.





