Semiconductor
Semiconductor
•The outermost orbit is called the valence shell.
• Electrons revolving round to the valence shell are called valance electrons.
• In solids, there are three energy bands.
•Energy band corresponding to valance electrons is called valence band (V.B.)
• Energy band corresponding to free electrons is called the conduction band (C.B.) •The energy band (gap) between the V.B. & C.B is known as the forbidden band (F.B.). Actually, the energy difference between the V.B. & C.B. is known as the energy gap denoted by Eg.
Conductor
• Energy gap between V.B. & C.B. is negligible (tends to zero).
•Valence band & conduction band are overlapped. No distinction between them
• Valence electrons are the valence shell is less than four.
• Both valence band & conduction band are partially filled.
•Valance electrons are easily conducted into the conduction band
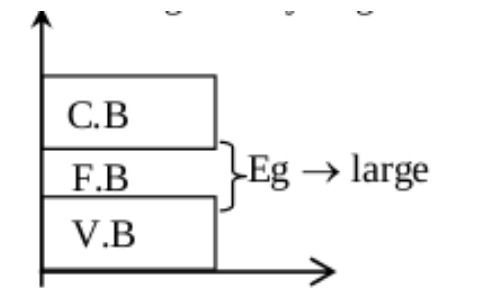
Insulators
•In the case of an insulator, the energy gap between V.B and C.B is generally large
• No valence electrons in the valence shell are more than four
• No valence electrons can reach the conduction band due to the large energy gap
• V.B is totally filled but the conduction band is empty
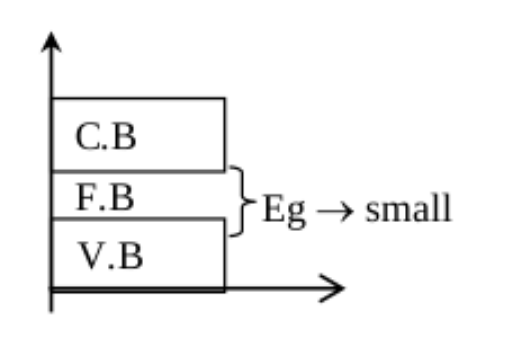
Semi-conductors
• Energy gap between V.B and C.B is small i.e less than an insulator but greater than the conductor
• At absolute zero, the semi-conductor act as an insulator
• Rise is temp ( electron cross the energy gap ) semi-conductor act like the conductor
• Valence electrons are the valence shall equal to four
• Materials whose all electrical properties lies is between a good conductor and an insulator
• Types of semi-conductors:
1. Intrinsic semi-conductors (Pure semi-conductor)
• Pure semiconductors are called intrinsic semi-conductor.
• Good examples are Si & Ge.
•Carrier concentrations are equal.
• Electrical conductivity is negligible.
• No remarkable use.
• Conductivity depends on only temperature.
2. Extrinsic semiconductors
• Impurity atoms are doped to a pure semiconductor, and an extrinsic semiconductor is formed.
• Impurity atoms having no four valence electrons are doped.
• Atoms having three valence electrons in the valence shell are called trivalent impurities eg. Aluminum, Indium, Gallium, etc.
• Atom having valence electrons equal to five are called pentavalent impunities. Eg. Phosphorus, Arsenic, Antimony, etc.
• Process of mixing of the impurities to the pure semiconductors, the phenomenon is known as doping.
• Mixed impurities are called doping agents. . According to the doping impurities to that of pure semi-conductors like Ge or Si.
• Extrinsic semi-conductors are two types
i. P-type semi-conductor
•When trivalent impurities are doped to pure Si or Ge, the p-types doped semiconductor is formed.
• Trivalent impurity atoms are acceptor type o So formed p-type is acceptor type semiconductor
• In the time of mixing of the impurity to the pure one more electron is accepted by the impurity from the
surrounding to complete its stable octet.
• A vacancy is created in the system that vacancy has the tendency to accept one electron known as a hole.
• In p-type, the majority are hole carriers.
• Minority are electron carriers.
• In P-type, current flow due to holes.
ii. N-type Semi-Conductor
• Pentavalent impurity atoms are doped to pre Si o Ge.
•Pentravalent impurities are donor-type impurities.
•During successive doping of pentavalent impunities to the pure semi-conductors many electrons are donated to the system.
• Majority are electrons carrier.
• Minority are holes carries.
• In N-type, semi-conductor, current flow due to electrons.
•Finally, due to the mixing of impurities, electrical conductivity increased in the case of extrinsic semi-conductors.
• Conductivity and resistivity depend on temp.

Rectification
• Rectification is the process of conversion of a.c. power into d.c. power.
• In a half-wave rectifier circuit, only one-half cycle of a.c. input is
obtained as d.c. output across the load resistor.
• In half-wave rectification, the output is pulsating (not smooth)
• In full ware rectifier both half cycle of a.c. input, are obtained as d.c. output across load resistor:
• Output is continuous (Smooth)
• For rectification purposes, we choose a full-waves rectifier circuit.