Use of pronouns
Pronouns Pronouns are words that are used instead of nouns.
There are 5 types of pronouns:
1. Subject pronoun
Rules:
a. The subject pronoun is used after the "be" verb auxiliary.
Example: It was they who completed the plan. It is she who solved the problem.
b. The subject pronoun is used in the subject position of the sentence
Example: He is doing his homework right now. I went to the cinema yesterday.
C. The subject pronoun is used with equal comparisons
Examples: She is as tall as I.(am) We are as strong as they (are).
d. If three persons are used for singular we use second person, third person, and first-person. For plural, we use first person, second person, and third person.
Examples: You, he and I went out. We, you and they arrived early.
2. Object pronoun
Rules
a. The object pronoun is used in the object position of the sentence.
Examples:
She gave me the keys to the door.
I lent her the pen.
b. The object pronoun is used with a preposition.
Examples:
The public is looking for them.
They discussed the problem with us.
c. It is used with equal comparisons
Example:
She ate as much food as them.
d. exception
Whenever 'let' is used use an object pronoun.
Example:
Let them do it.
e. If an adjective is used then we use the subject pronoun. If an adverb is
used then we use the object pronoun.
Examples:
She is taller than l(am).
He arrived sooner than me.
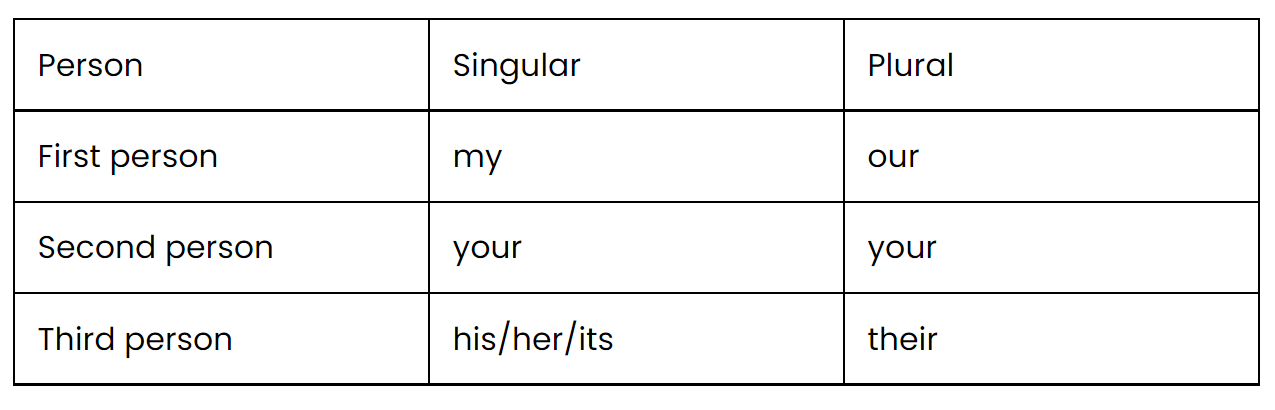
3. Possessive adjective
A possessive adjective is not a pronoun because it doesn't replace a noun. It modifies the noun.
Examples:
This is my pen.
It is our school.
4. Possessive pronoun
A possessive pronoun can only be used after using a possessive adjective.
Ecamples:
This is my pen. It is mine.
It is our school. It is ours.
5. Reflexive pronoun